TEMA Standards are worldwide accepted as the authority on shell and tube heat exchangers design and manufacturing. These standards are the most commonly used in a wide range of industries throughout the world: refineries, oil and gas, power generation, etc.
The acronym TEMA stands for “Tubular Exchangers Manufacturers Association”, it is a trade association of leading manufacturers of shell and tube exchangers who have been pioneers in the research and development of heat exchangers. The association meets regularly to update its published standards, respond to some inquiries, and discuss about the topics related to the industry.
TEMA Standards define the style of heat exchangers and the machining and assembly tolerances. They are divided in three major classifications, related to its duty:
- TEMA C – General Service
- TEMA B – Chemical Service
- TEMA R – Refinery Service
As there are many variations in mechanical designs for front and rear heads and shells, TEMA designations correspond to each major type of front head, shell type and rear head. For example, in TEMA Type BEM, letter “B” identifies the front head, letter “E” identifies the middle section (shell design) and letter “M” identifies the rear head.
Removable Bundle, Internal Split Ring Floating Head: : Type AES, BES, etc.
These designs are recommended when frequent tube bundle removal is necessary. They are more favourable to thermal shock than AEW or BEW designs and they are also suitable for volatile or toxic fluids.
Advantages:
- Floating head design allows thermal expansion
- Higher heat transfer surface area than pull-through designs (AET or BET Types)
- Available to multiple passes on tube side
Limitations:
- Shell cover, split ring and floating head cover must be removed to remove the tube bundle, which results in higher maintenance costs
Applications:
- Chemical processing applications for toxic fluids
- Special gas after coolers and intercoolers
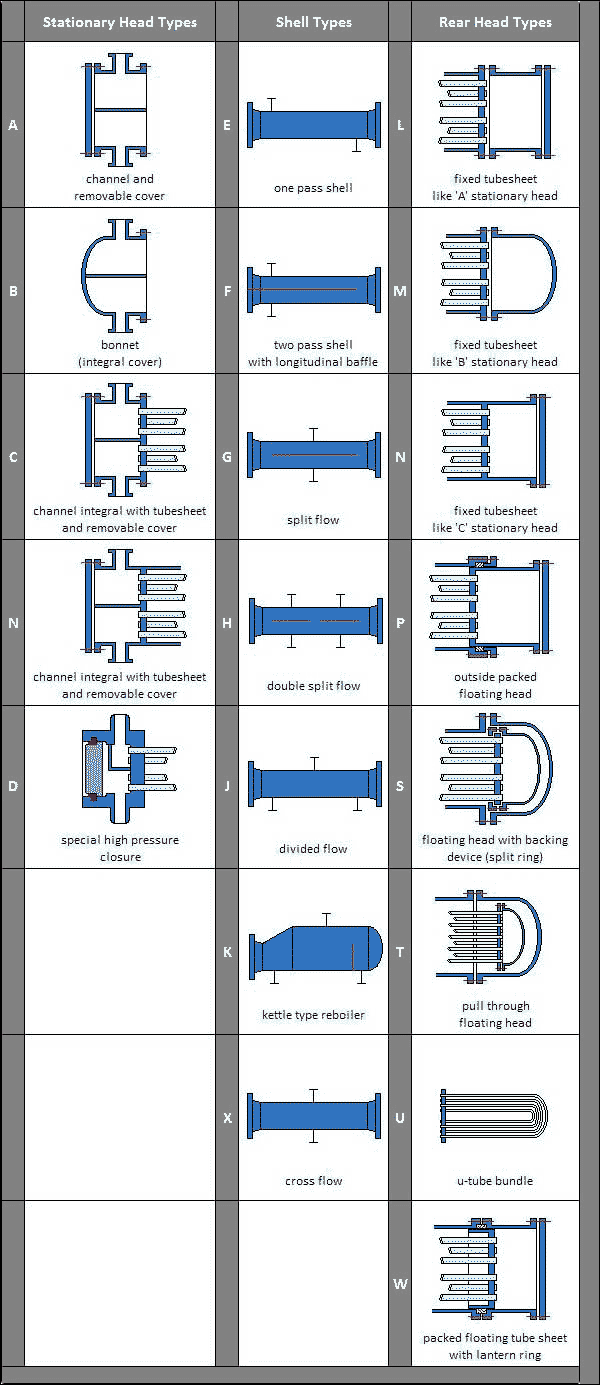
Straight Tube and Fixed Tube Sheet: Type BEM, AEM, NEN, etc.
This design is the simplest design and usually more economical. The tube sheet is welded to the shell, while heads are bolted to the tube sheet.
Advantages:
- More economical than removable bundle designs
- Capable of multiple pass designs
Limitations:
- Chemical solution is need to clean the shell side
- No capacity to absorb thermal expansion between the outer shell and tube bundle
Removable Bundle, Pull Through Floating Head: Type AET, BET etc.
These types of design are the best option for applications when frequent tube bundle removal is necessary because the floating head is bolted directly to the floating tube sheet. This allows the bundle to be pulled at the same with the head.
Advantages:
- Floating head design allows thermal expansion
- Shell side can be inspected and mechanically cleaned
- Large shell side nozzle entrance area for proper distribution over the bundle
- Multiple tube side passes available
- Suitable for volatile or toxic fluids
Applications:
- General industrial applications requiring frequent cleaning
- Chemical processing applications for toxic fluids
- Hydrocarbon fluid condensers
Removable Bundle, U-tube: Type BEU, AEU etc.
This design is recommended for high thermal shock applications, as each tube can expand and contract independently and u-tube bundles are normally very economical. It is usually the best option for maximum thermal expansion applications.
Advantages:
- U-tube design allows differential thermal expansion between the shell and the tube bundle as well as between individual tubes
- Capacity to handle high thermal shock applications
- More economical design for removable bundles
- Shell side can be inspected and mechanically cleaned
- Bundle can be removed from one end for cleaning or replacement
- Multiple tube side passes are available
Applications:
- Optimal for steam to liquid applications
- Chemical, oil and water heating applications
CADE Engineering Services for TEMA Heat Exchangers Design
- Thermal / hydraulic design
- Mechanical design
- Fluid-dynamic simulation (CFD)
- Thermo-structural simulation by finite elements (FEM)
- Detailed engineering (manufacturing drawings)
- Technical purchasing management (procurement)
- Dimensional control with point cloud
- In service failure analysis
- Integrity and remaining life assessment. Fitness for Service
Further information:
For any question or further information request about heat exchangers design or engineering assessment services, please complete the following form: